题目大意:给定一个长度为 $n$ 的非负整数序列,将其划分成 $k+1$ 段,划分一次的得分是左右两个新产生的块的元素和的乘积,求最大分数,并输出任意一种划分方案。$n \leq 100000, k \leq \min(n-1, 200)$
设 $f[i][j]$ 表示长度为 $i$ 的序列划分了 $k$ 次的最大分数,$s_i = \sum\limits_{j=1}^{i}a_i$
以下省略第二维,假设 $s_j > s_k$,考虑
设 $x_i = s_i, y_i = s_i^2-f[i]$,对于每个 $s_i$,找出平面上一个满足上式的点 $(x_j,y_j)$。
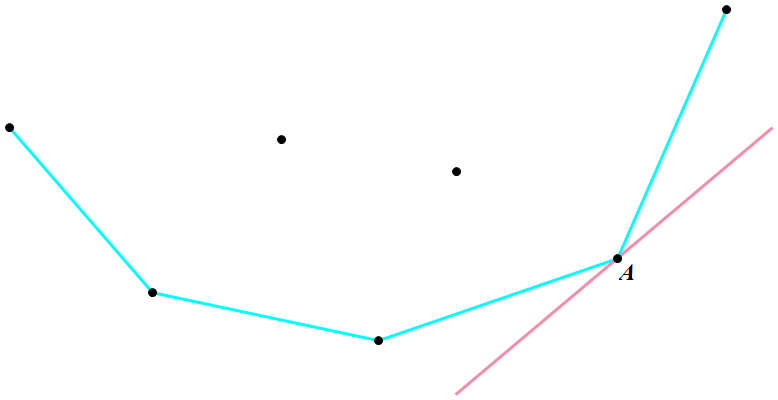
如何找出这个点?维护下凸壳,用斜率为 $s_i$ 的直线去卡,假设为粉色实线,那么答案就是点 $A$,单调队列维护。注意判断 $s_j=s_k$ 的情况。
没有卡 128MB 空间版本:
#include <cstdio>
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100001, M = 201;
struct Node {
LL x, y; int z;
} q[M][N];
int head[M], tail[M], id[N][M]; LL s[N];
int read() {
int x = 0; char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') c = getchar();
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
int min(int x, int y) {
return x < y ? x : y;
}
double slope(Node a, Node b) {
if (a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y ? -1e18 : 1e18;
return 1.0 * (a.y - b.y) / (a.x - b.x);
}
void print(int i, int j) {
if (!id[i][j]) return;
print(id[i][j], j - 1);
printf("%d ", id[i][j]);
}
int main() {
int n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) s[i] = s[i-1] + read();
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++i) head[i] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { //长度为i
Node now;
for (int j = min(m, i - 1); j; --j) { //划分j次
while (head[j-1] < tail[j-1] && slope(q[j-1][head[j-1]+1], q[j-1][head[j-1]]) <= s[i])
++head[j-1];
LL res = s[i] * q[j-1][head[j-1]].x - q[j-1][head[j-1]].y;
id[i][j] = q[j-1][head[j-1]].z;
if (i == n && j == m) printf("%lld\n", res);
now = (Node){s[i], s[i] * s[i] - res, i};
while (head[j] < tail[j] && slope(q[j][tail[j]], q[j][tail[j]-1]) >= slope(now, q[j][tail[j]]))
--tail[j];
q[j][++tail[j]] = now;
}
now = (Node){s[i], s[i] * s[i], i};
while (head[0] < tail[0] && slope(q[0][tail[0]], q[0][tail[0]-1]) >= slope(now, q[0][tail[0]]))
--tail[0];
q[0][++tail[0]] = now;
}
print(n, m);
return 0;
}
优化空间版本:
#include <cstdio>
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100001, M = 201;
struct Node {
LL x, y; int z;
} q[2][N];
int head[2] = {1, 1}, tail[2], id[N][M]; LL s[N];
int read() {
int x = 0; char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') c = getchar();
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
int min(int x, int y) {
return x < y ? x : y;
}
double slope(Node a, Node b) {
if (a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y ? -1e18 : 1e18;
return 1.0 * (a.y - b.y) / (a.x - b.x);
}
void print(int i, int j) {
if (!id[i][j]) return;
print(id[i][j], j - 1);
printf("%d ", id[i][j]);
}
int main() {
int n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) s[i] = s[i-1] + read();
for (int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) { //划分j次
head[j&1] = 1, tail[j&1] = 0;
for (int i = j + 1; i <= n; ++i) { //长度为i
int p = j & 1 ^ 1;
while (head[p] < tail[p] && slope(q[p][head[p]+1], q[p][head[p]]) <= s[i])
++head[p];
LL res = s[i] * q[p][head[p]].x - q[p][head[p]].y;
id[i][j] = q[p][head[p]].z;
if (i == n && j == m) printf("%lld\n", res);
Node now = (Node){s[i], s[i] * s[i] - res, i};
while (head[j&1] < tail[j&1] && slope(q[j&1][tail[j&1]], q[j&1][tail[j&1]-1]) >= slope(now, q[j&1][tail[j&1]]))
--tail[j&1];
q[j&1][++tail[j&1]] = now;
}
}
print(n, m);
return 0;
}
时间复杂度 $O(nk)$